To Protect and Preserve: A Discussion on the Ethics of Caring for Art & Historic Landmarks.
Ruth Osborne
Last Wednesday evening, I had the opportunity to present on past, present, and future wrongs done to art, before an engaged and impassioned audience at The Coffee House Club in midtown Manhattan.
Historic preservation and issues of transparency and careful stewardship of the arts are inherently linked with the original aims of ArtWatch International, an organization founded when a renowned art history scholar was taken to court for “aggravated slander” against a harmful conservation treatment upon a significant work of the Italian Renaissance. That scholar was Professor James Beck, and the work was the tomb of Ilaria del Carretto by Jacopo della Quercia. Beck ultimately came out the victor, but the opposition was strong and well-connected.
Beck’s final statement at the trial read:
“The possibility that the considered observations of art critics and art scholars should not be aired, or that their judgments need to be cloaked in palliative euphemisms if they are expressed at all, is a dangerous precedent for the principle of free speech and free criticism. If such rights, which are guaranteed by the world charter of the United Nations and by the constitutions of both the United States and Italy, among others, were qualified, the effect would be chilling, and certainly the true losers would be the art objects of the past and future generations who have every right to expect to enjoy and learn from the treasures of the culture, conserved and preserved, in the best manner possible.”
The ultimate goal of the Ilaria case and other such struggles ArtWatch International has subsequently undertaken is not only to argue for the care of these sites and objects in the proper way, and thus ensure the history they represent is not carelessly swept away. It is also our aim to heighten transparency and create a dialogue about the treatment (or damage) done upon works of art, something often amiss in public statements by those placed in roles of protecting and preserving our cultural heritage. When there exist such individuals as Beck and others who are willing to speak out against wrongdoing and injury, the memory and enjoyment of our cultural heritage has hope of protection.
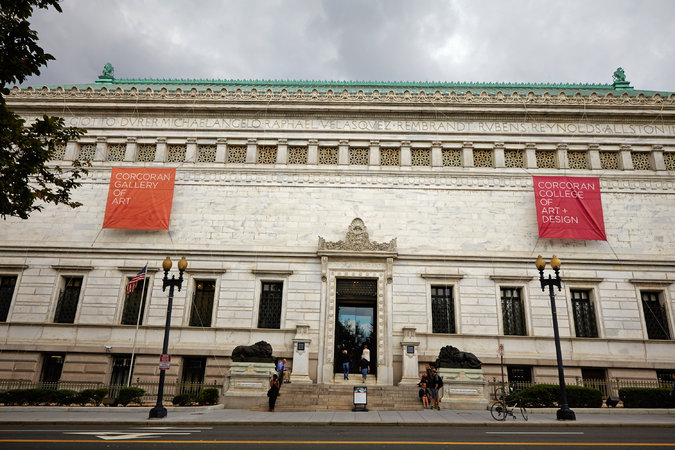
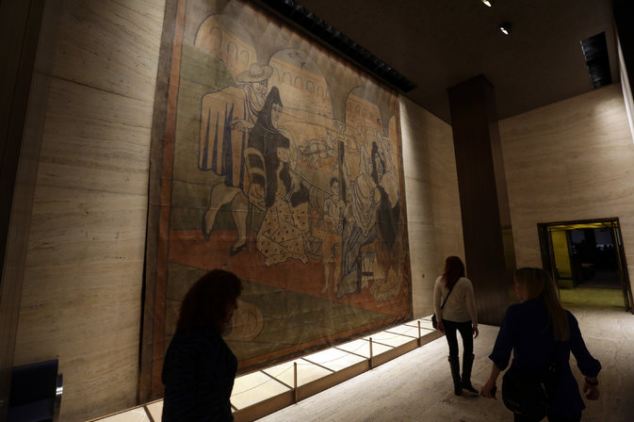
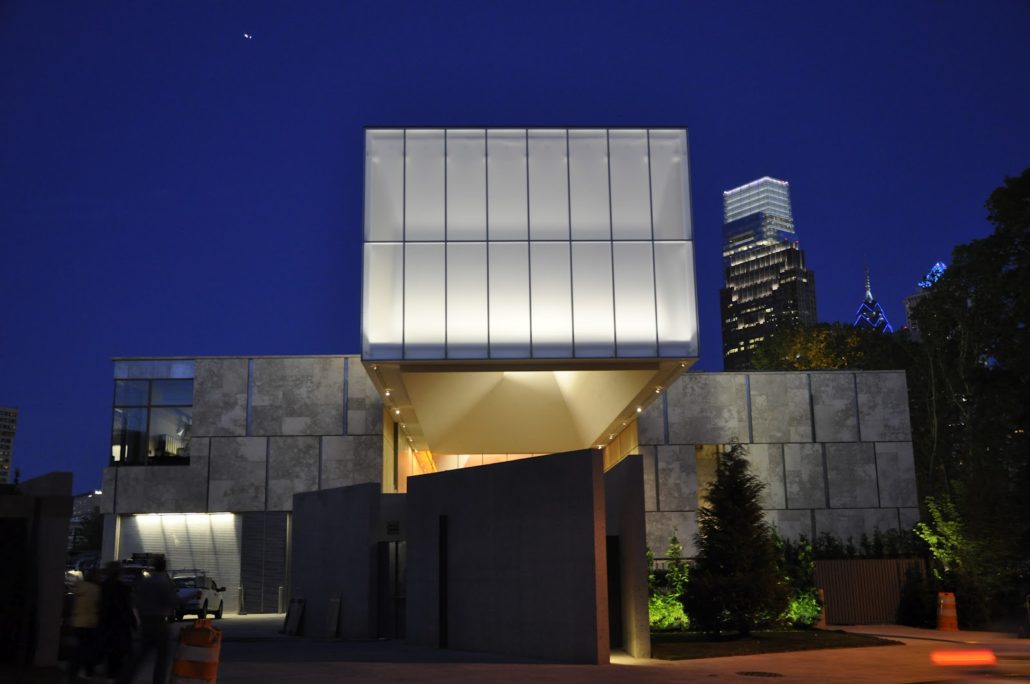
The issues of the Barnes Collection (1990-2012), Corcoran Gallery of Art (2012-2014), the Merchant’s House Museum (2012-2015), and the Delaware Art Museum (2014-2015) relate the disconcerting fact that there is a growing need to fight against damage to art and history. From these examples, one can also see how the law protecting art, collections stewardship, and historic preservation has attempted to help, but unfortunately in many cases has lost the battle. Awareness about the dangers posed to historic preservation and good collections care and management is a necessity. Collections are being separated from original donors’ intentions, from their historic environments, sent around the world incurring damage in transit. Historic structures are being discarded and treated as second-class citizens of a city’s landscape in the face of new development. There must be individuals who remind those in power – board trustees, directors, museum professionals, city planners – that they also have a responsibility to provide protection for our artistic and cultural heritage. By disregarding it, they are doing their work without heart. They are doing a disservice to both their industries and themselves. These paintings, sculptures, and historic sites are delicate and require careful stewardship and attention in order to be honored and preserved for discovery by present and future generations.
The hope of ArtWatch is that we can provide a platform on which concerns can be aired and best practices championed and maintained