Calder Mobile Disappears: Will this be the next item sold by the Delaware Art Museum?
Ruth Osborne
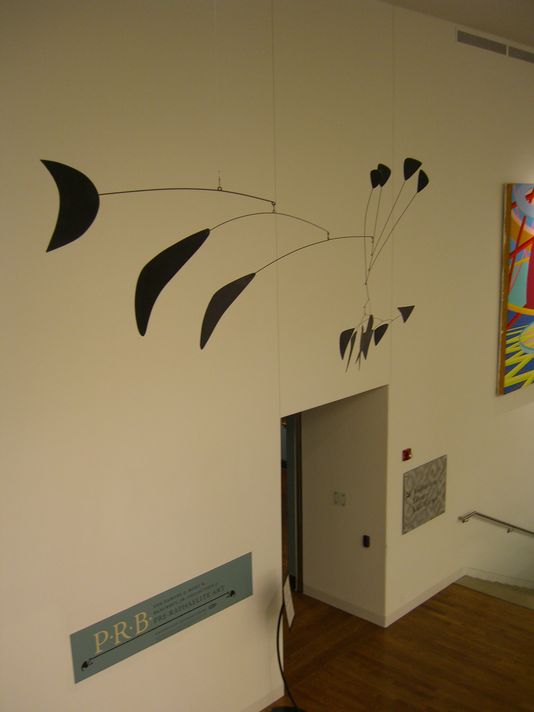

Alexander Calder’s Black Crescent, as it hung in the East Court at the Delaware Art Museum. Courtesy: Matt Freeman/The News Journal
The Delaware Art Museum may be best-known for its nineteenth-century works (by the Pre-Raphaelites, Brandywine River School, and Ashcan School), but their modern collection may also take a hit from the recent budget crisis. Recent speculation by local news sources suggests the disappearance of an Alexander Calder mobile from installation and the Museum’s online database heralds this will be the next of the possibly four items to be sold.
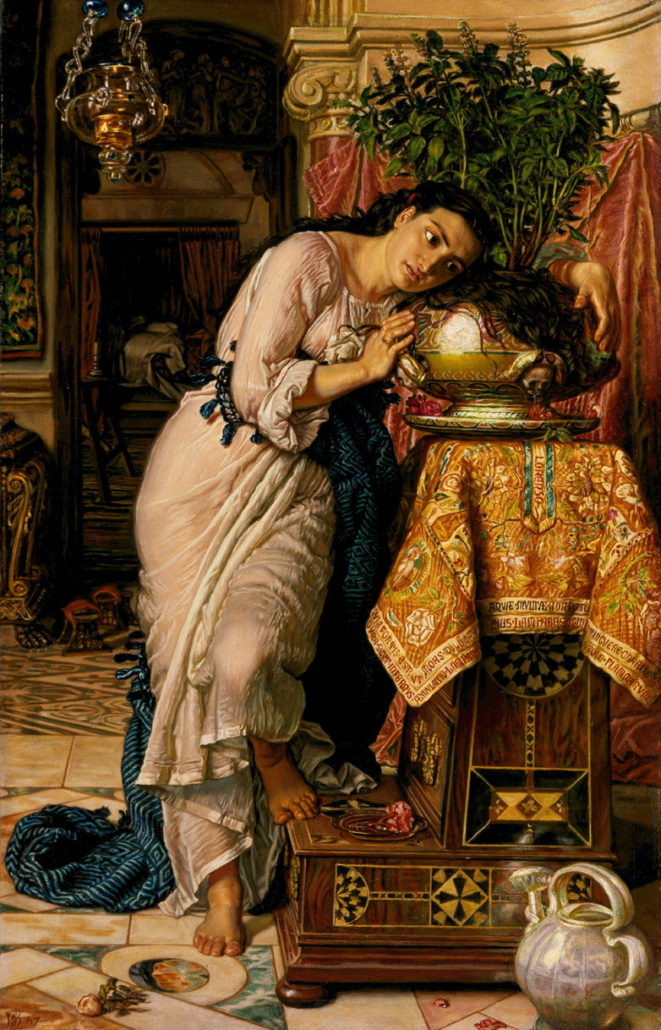
“Black Crescent” (1959), purchased by the Museum in 1961, will need to bring in upwards of $10 million to help cover the $30 mil. needed to replenish its endowment and pay off construction costs from the previous decade. As recent sales have shown, Calder pieces have certainly gone for as much, if not more (most notably, last month’s “Poisson Volant” for $26 mil. at Christie’s).
While we await the June 17 sale of William Holman Hunt’s Isabella and the Pot of Basil, even more criticism has emerged from a national public whose trust has been deceived by the Delaware Art Museum. Former AAMD President and Director of the PMA Timothy Rub recently wrote in The Wall Street Journal:
“This is not a matter, as is often claimed, of protecting the public trust, as important as that may be. Rather, it is about common sense. You don’t cut out the heart to cure the patient; and yet this was the remedy chosen by Delaware’s trustees to restore their institution to good health. Regrettably, they seem not to have understood their broader responsibility to care for all of the museum’s assets—most significantly, its collection.
It is precisely in such circumstances that the trustees of the Delaware Art Museum should have stood up—and stood together—to champion a broader and more compelling vision of cultural stewardship by protecting their collection rather than monetizing it. That they did not do so is unfortunate for their institution and has set a dangerous precedent for the field.“
As we pointed out last week, such activity in the museum world in response to the recent economic crisis has unfortunately forced several museums to make such ill-advised decisions. The true character of a Board is shown when their museum is faced with financial strain. ArtWatch hopes that, while these actions by the Delaware Art Museum demonstrate one type of reaction, museum trustees elsewhere will take such opportunities to care for the collection first, and a reputation-bolstering expansion second.